Some essential notes on C-statistics
Basic concepts
C-statistics is based on Poisson likelihood:
where
Omitting the factorial term, we can get the Cash-statistics (Cash 1979):
Approximating the factorial term by Stirling's formula, that is
a modification of the original Cash-statistic, C-statistics, can be obtained as follows:
which is implemented in some popular fitting packages like XSPEC (Arnaud 1996), SHERPA (Freeman et al. 2001), and SPEX (Kaastra et al. 1996).
Assuming that there are
A simple schematic
For simplicity, we may as well take a model with just two parameters
The line segment AD represents the
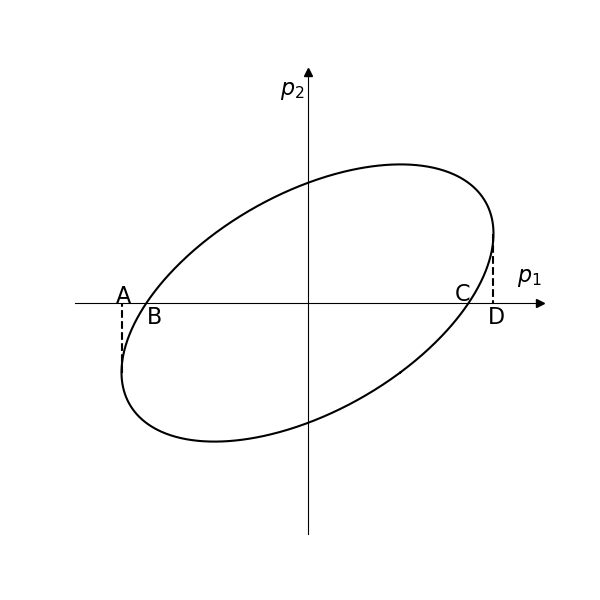
The
The algorithm of finding the
As shown in the Figure, you may think that we need to get the boundary, namely, the oblique ellipse first and then get the
- Get the best-fit parameter set
- Fix the parameter
to a value that is close to the but free all the rest parameters.
- Fix the parameter
- Obtain the minimum
- Obtain the minimum
- If the minimum
is larger than , choose a new that is closer to , if the minimum is smaller than , choose a new that is farther from . Go to step 2.
- If the minimum
- Return the two points
that can result in the minimum being equal to by setting the rest parameters to be free. Actually, it is not exactly , there is some tolerance, the algorithm in SPEX will stop at some value that is close to , like .
- Return the two points
Why the
Why it is
is distributed like a
is approximately distributed like a